
- info@xbyteanalytics.com
- +1 832-251-7311
- Home
- Services
- Data Analytics Consulting
- Data Warehousing Consulting
- Data Visualization Services
- Business Intelligence Services
- Data Analytics Applications
- Data Governance Consulting Services
- Self-Service Business Intelligence
- Cloud-based Data Warehousing
- Targeted Predictive Analytics
- Managed Data Services
- Data Ecosystem Modernization
- Data Governance
- Data & Analytics Assessment
- Data & Analytics Consulting
- Cloud Migration & Modern Cloud Architecture
- Master Data Management
- Alternative Data
- Data Pipeline & Transformations
- Industries
- Work
- Company
- Home
- Services
- Data Analytics Consulting
- Data Warehousing Consulting
- Data Visualization Services
- Business Intelligence Services
- Data Analytics Applications
- Data Governance Consulting Services
- Self-Service Business Intelligence
- Cloud-based Data Warehousing
- Targeted Predictive Analytics
- Managed Data Services
- Data Ecosystem Modernization
- Data Governance
- Data & Analytics Assessment
- Data & Analytics Consulting
- Cloud Migration & Modern Cloud Architecture
- Master Data Management
- Alternative Data
- Data Pipeline & Transformations
- Industries
- Work
- Company
Unlocking Insights: Detailed Guide to Data Visualization

Introduction
Before the data shows up in pretty pictures, a lot is happening behind the scenes. This setup, known as a data pipeline, is like the foundation. A big part of this setup is the Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process and its tools – think of it as the behind-the-scenes work for any BI system. Then, the part where you finally see the data in an excellent visual way is like the front end, where users get to see and play with the data.
Compared to other activities, data visualization is an effortless task. However, presenting your facts correctly is a skill that might make the difference between your project being approved or denied. Every tiny detail matters if you want your visualization to stand out from the competition.
What is Data Visualization?
The process of transforming unprocessed data into a graphical representation is known as data visualization. This unprocessed data can be text, numbers, or symbols. The objective of the data visualization is to establish inclinations, trends, and patterns, and to demonstrate logical links between units. Visualization can be done in a format that works for the data, depending on the kind of logical link.
Businesses provide expert data visualization consulting services by adopting advanced solutions. Most of the time, graphics are made by hand using the appropriate program, such as Photoshop or PowerPoint. Yet the discipline of analytics continues to be its primary application.
What are its distinguishing features?
- Determine which areas require improvement or attention.
- Describe the elements that affect consumer behavior.
- Ability to make decisions.
- Integration Proficiency.
- Forecast the amount of sales.
Benefits of Data Visualization
Data visualization helps businesses in numerous manner. It makes the data presentation more effective and easy to understand.
Let’s understand the benefits of data visualization.
- Simplifies Complex Data:
- Reveals Patterns and Trends:
- Aids in Decision-making:
- Storytelling:
- Increased Engagement:
- Improved Collaboration:
Charts, graphs, and pictures are used in visualizations to present complicated data in an understandable manner. This allows everyone to grasp the essential ideas rapidly. It does this by avoiding large amounts of data.
Visualizations simplify seeing key patterns and trends in a sea of data. Using colors, shapes, and trends, we can rapidly identify what’s essential. This is essential for making decisions based on what the data tells us.
Visualizations provide a quick summary of important information. Decision-makers can rapidly grasp the essential themes without getting bogged down in minute details. This quickness is critical for making rapid judgments based on accurate information.
Data visualizations convey a narrative. Data storytellers lead their audience through the material by mixing images with a story and stressing key elements. This method of narrative makes the facts more intriguing and memorable.
Visualizations capture people’s attention more effectively than raw data. Colors, charts, and interactive components keep viewers interested and inspire them to dig deeper into the data.
Visualizations serve as a common ground for teams with diverse skills. Team members can view and discuss visual information more easily when they work together. This fosters a culture of collaboration and mutual understanding.
Data Visualization Techniques & Types
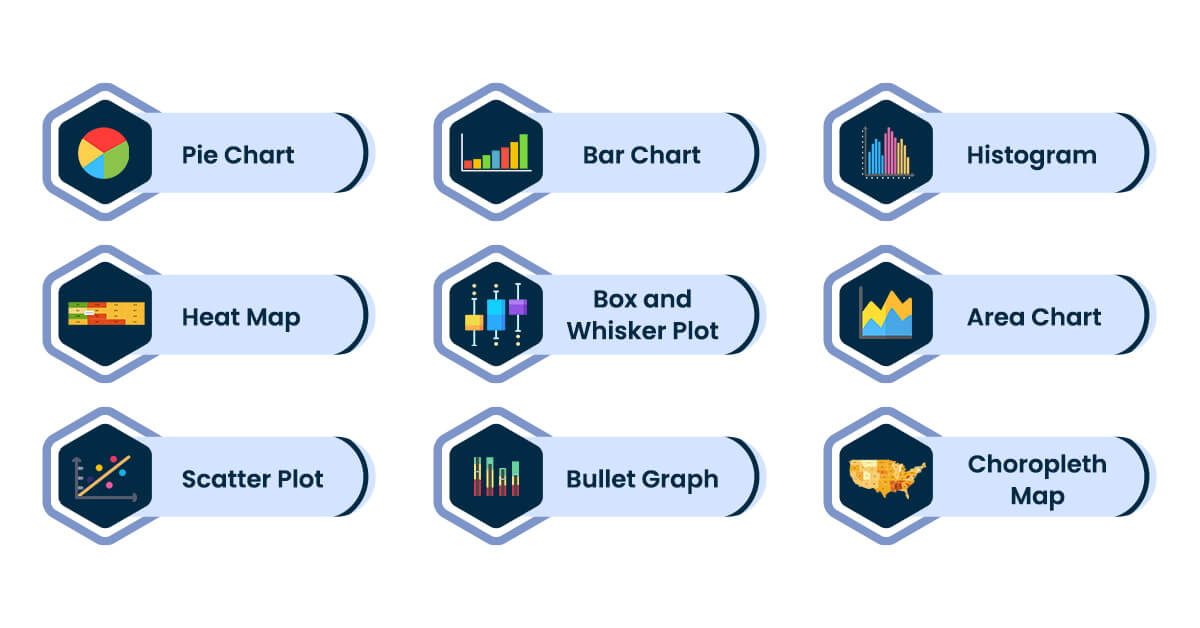
The data visualization techniques depend on the sort of data you’re working with and the story you’re telling with it. The well-defined techniques serve as the key components of data visualization.
Here are some fundamental types of data visualization and techniques to present the data:
1. Pie Chart
One of the most popular methods of data visualization is easy-to-use data visualization methods, pie charts are utilized in numerous scenarios. Pie charts are perfect for showing comparisons between parts and wholes or proportions. It works well for audiences who need to become more familiar with the content or who are interested in the main points.
Key Points:
- It is comparatively simple to understand.
- Adequate for showing complicated data to visitors who need a more in-depth explanation of the data.
- It can also used to show the division of a categorical variable into its several divisions.
2. Bar Chart
A user-friendly technique for data visualization is the traditional bar chart, often known as a bar graph. This kind of visualization displays a measured value on one axis of the chart and the categories being compared. The length of the bar represents how each group performs with the value.
One disadvantage is that labeling and clarity can become problematic when too many categories are included. Businesses frequently use bar charts to compare data, such as the income of various areas or the market shares of various brands. Bar charts come in various forms with unique features.
Key Points:
- Bar charts are often used due to their ease of reading.
- Customized to display more intricate data models because of their versatility.
- Chart arranged in clusters to show distribution across market segments or item subcategories.
- This also applies to horizontal bar charts, where lengthy data labels fit better on the bars.
3. Histogram
The histogram is one of the most often used representations for examining data distribution. They use bars to display the distribution of the numerical variable.
The numerical data is first split into many ranges or bins, and the frequency of occurrence of each range is tallied to create a histogram. The vertical axis shows the frequency or percentage of occurrences of a range. The horizontal axis displays the range.
For example, you can use a histogram to display the number of clicks your website received daily throughout the previous week. Using this display, you can rapidly ascertain which days on your website had the most and least clicks.
Key Points:
- It shows the distribution of data across a continuous interval or predetermined duration.
- Finding gaps or anomalous values, as well as areas of concentrated values is made easier with the aid of these representations.
- When displaying the frequency of an event, histograms are very helpful.
4. Heat Map
A heat map is a data visualization technique where different colors are used to represent different data points. A user can only read and interpret a heatmap with a clear legend.
For instance, you can use a heat map. It plots the day of the week on the vertical axis and the time of day on the horizontal axis.
You can use it to determine when the business has the most sales. Then, you can look for trends in the data that will allow you to determine the exact times of day. Use color to shade the matrix, with hues corresponding to the amount of sales at different times when your store is busiest.
Key Points:
- A popular and elegant matrix plot that can visually represent the relationship between two variables is a heatmap.
- These charts employ color to convey values in a way that makes it simple for the audience to spot trends immediately.
- A color code indicates the level of connection between two variables.
5. Box and Whisker Plot
The quartiles of the data are used to provide a visual overview of the data in a box and whisker plot, or box plot. Initially, a box is made in the data set from the first to the third quartile. A line inside the box shows the median. Next, lines that connect the box to the lowest and maximum extreme are drawn, called “whiskers.” Single points that match the whiskers are indicative of outliers.
Key Points:
- This kind of chart offers a readily understood visual overview of the data set.
- It is also helpful for rapidly determining if the data is symmetrical or skewed.
- A color code indicates the level of connection between two variables.
6. Area Chart
An area chart, also known as an area graph, is a line graph representing the entire value of every data point by shading the area below the line. Stacked area charts are used when various data series need to be compared on the same graph. This type of data visualization helps display how one or more values change over time and how each item works together to get the total. Below is an example of an area chart that tracks the P/E ratio. This financial analytics indicator compares a company’s share value to a standard set by the industry (second variable). It gives investors an estimate of the price they would pay for each dollar of earnings in stock shares.
Key Points:
- It is ideal for illustrating the evolution of various values over time.
- It illustrates how numerical values vary depending on a second variable by combining a line and bar chart.
- Part or full proof comparisons can be effectively displayed using stacked area charts.
7. Scatter Plot
A scatter plot is another common way of displaying data. A scatter plot represents information about two variables as points placed on the horizontal and vertical axes. This form of data visualization is useful for illustrating the relationships between variables and identifying patterns or correlations in data.
This style of representation is based on X and Y axes. Between them, dots are added to define objects. As with line graphs, dots put between the axes are detected in a moment. The only constraint to this display form is a certain amount of axes.
Key Points:
- Scatter plots work well for big data sets since more data points make it simpler to discern trends.
- The closer the data points are clustered, the greater the connection or trend becomes.
- The position of a dot on the graph indicates the attributes it possesses.
8. Bullet Graph
A bar graph variant known as a bullet graph can serve as a substitute for dashboard gauges in the display of performance statistics. The primary purpose of the bullet graph is to show how a company is doing with established benchmarks for essential business KPIs to the audience. In addition, range scores like “poor,” “fair,” or “good” are represented by the segmented colored parts behind the horizontal bar.
Key Points:
- A bullet graph represents a comparable value, or target, by the vertical line.
- The actual value is represented by the darker horizontal bar in the center of the chart.
- The goal for that measure has been attained if the horizontal bar crosses the vertical line.
9 . Choropleth Map
A choropleth map displays numerical values using color, shading, and other patterns. This data can be displayed by combining data from different geographic regions. These illustrations use a color progression on a spectrum. This color separation can be done by shading to distinguish high and low values.
Key Points:
- Using data visualization tools, maps can be made interactive so that users can get precise values.
- Viewers can use choropleth maps to observe how any variable differs from one region to the next.
- The drawback is that it becomes difficult to retrieve precise numerical data.
Top Data Visualization Tools
To make the representation more effective and helpful, experts can utilize various Data Visualization technologies and tools:
1. Tableau
Tableau is one of the most popular data visualization solutions on the market for two key reasons: It’s simple to use and highly effective. The application can create various display styles, including charts and maps. It accepts unstructured data inputs from various sources to display in structured form. Tableau offers an analytics platform and customer relationship management (CRM) software. It provides various versions for desktop, server, and web-hosted versions.
There’s also a free option known as Tableau Public. It is essential to consider that everyone can view the data on the free visualization version. This makes it a decent choice for learning the basics of the software. However, it is not suitable for any sensitive or confidential information.
Core features
- Data connection and import:
- Data visualization:
- Dashboard creation:
- Data blending:
Importing and connecting to data sources is possible with Tableau. These sources might include databases, spreadsheets, cloud services, and other large data sources. You may use this to import and modify data for analysis.
Bar charts, line charts, scatter plots, and maps are just a few of the many visualization possibilities that Tableau provides. Interactive visualizations are a useful tool for exploring and comprehending your data.
To get a thorough perspective of your data, you may integrate several visualizations into dashboards.
You may combine data from several sources using Tableau. This is especially helpful when working with data that comes from many systems or databases.
2. Looker
With Google’s Looker, business users can create integrated apps, generate dashboards and reports from many data sources, and optimize processes with real-time insights. Looker is a unified and self-service analytics platform. Looker enables integration with open-source programs via the Google Cloud Platform. Consequently, BigQuery ML, AutoML, and Vertex AI can be used to enhance its data processing capabilities.
Core features
- Self-service data visualizations:
- Ad hoc reporting:
- Real-time view of your data:
Looker enables you to build custom data models, set metrics, and construct dashboards and reports. It uses LookML to deliver data experiences.
You may use Looker’s semantic model to study, examine, and display data more interactively. This connection enables ad hoc reporting, which helps you to identify irregularities.
Looker allows you to get real-time insights from the cloud of your choosing. You may also tweak data by adding and changing filters.
3. Zoho Analytics
Zoho Analytics is best data visualization tool for professionals who want to visualize business analytics. You can prepare, visualize, and explore data with Zoho Analytics. Because of this, it’s widely used to create aesthetically pleasing dashboards. These can display the data on sales, marketing, profit, revenues, expenses, and pipelines of the business.
The platform is currently used by two million consumers and more than 500,000 enterprises. With the analytics mechanism, it becomes easy to track key performance indicators. It helps identify trends, project future events, and uncover unrecognized data. With its AI-infused platform, Zoho Analytics provides a library of pre-made templates.
Core features
- Data integration:
- Data visualization:
- Data Preparation:
- Augmented Analytics:
Spreadsheets, cloud databases, and web apps are just a few examples of the business tools and data sources from which Zoho Analytics may import data.
A variety of prebuilt visualization templates, including as dashboards, pivot tables, charts, and graphs, are available with the application. Due to the low-code interface, you don’t need to be technical to build customized reports.
Data enrichment and transformation capabilities are provided. To prepare your data for analysis, you may calculate, build custom metrics, and merge datasets.
It uses AI, ML, and NPL technologies to provide you suggestions and contextual insights. What-if analyses and trend forecasting are also possible using the platform’s predictive analytics features.
4. ThoughtSpot
ThoughtSpot is an analytics powerhouse specializing in AI-driven, self-service analytics and data visualization. Beyond that, its brilliance continues to allow people to find insights. Users can analyze data easily by using common language searches. The slick, contemporary liveboards provide a portal to real-time data understanding. There’s more to do than see static charts. Liveboards help with data-driven decision-making and smooth data transfer.
Core features
- Interactivity:
- Data Integration:
- Mobile-friendly:
- AI-powered Search:
To obtain deeper insights, you may work with Liveboards, apply filters, dive down, and examine various parts of your data. Your data analysis and comprehension will be made simple for you by the tool’s interactive features.
You may combine data from several sources into a single dashboard by using liveboards. By establishing connections with databases, spreadsheets, cloud data sources, and even other databases, this offers a comprehensive picture of your data.
Liveboards make it simple for you to get data and insights while on the go since they are made to be adaptable and available on mobile devices.
ThoughtSpot Sage uses artificial intelligence to help you identify data trends and patterns so you can extract insightful information from your data.
5. Power BI
Power BI is an advanced data visualization tool created by Microsoft. It majorly works with other Microsoft applications and data visualization technologies. It helps in data modeling and offers a range of presentation alternatives. It includes simple presentation charts and intricate visualizations. Businesses that rely on Microsoft’s ecosystem broadly use Power BI. Despite its simple interface, Power BI takes analytical skills to function effectively.
Core features
- Interactive dashboards and reports:
- Visualizations:
- Change analysis:
- Data modeling:
A drag-and-drop interface allows you to create interactive dashboards and reports.
The default visualizations are charts, maps, and graphs. You may utilize Power BI’s custom visuals SDK if you need customized graphics.
Power BI suggests plausible causes for increases or reductions in attribute values and displays the findings within the visualization context.
Using Power BI tools such as Power Query and Power Pivot, you can shape and clean your data, construct relationships, and generate calculated measures with DAX.
6. Qlik Sense
Business users can examine data with the analytics platform Qlik Sense. It is highly regarded for its distinct analytical powers and adaptability to both on-premises and cloud implementations. Qlik Sense is a cutting-edge tool that helps users gain insights and make decisions quickly.
Core features
- Comprehensive Data Visualizations:
- Augmented Analytics:
- Real-time Data Pipeline:
- Hybrid Deployment Options:
Qlik Sense allows you to improve contexts, make discoveries, and build interactive representations.
This technology enables business users to ask complicated questions about their data. You may also use AutoML and predictive analytics to find important drivers in your data.
Qlik Sense includes reporting capabilities like as alarms, trigger automation, and monitoring.
The tool supports connections from a variety of sources, including public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises environments.
7. Sisense
Businesses can generate insights by gathering data from various sources by using data visualization services by Sisense. It is well known for its integrated analytical features. These features include RestAPI access and open-source integration. Evaluations have indicated that significant training is required for installation and configuration. This is because of the complexity of installing data cubes. It can take longer to become familiar with the platform and make use of all of its capabilities.
Core features
- Data Integration:
- Data Modeling:
- Data Visualization:
- Ad-hoc Analysis:
Sisense integrates data from several sources, such as databases, cloud services, and spreadsheets, for easy analysis.
Sisense offers data transformation, cleaning, and modeling capabilities. You prepare data for analysis by establishing relationships, generating computed fields, and executing data cleansing procedures.
Sisense offers a variety of data visualization choices, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards.
The tool’s ad-hoc query feature enables easy data exploration, report creation, and visualization without requiring technical skills.
8. Domo
Domo is a data visualization solution that delivers insights for decision-making. It facilitates strategic decisions after performing in-depth data analysis. It facilitates question-answering, forecasting, and what-if scenario planning. Domo provides support and assistance as and when required. This was first designed for analysts only but now helps developers and designers.
Core features
- Visualizations:
- Customizable dashboards:
- Data Modeling:
Domo offers a variety of chart styles and custom maps to help you see your data and build dashboards.
A low-code environment enables you to develop dashboards and reports without prior technical knowledge. Dashboards may be further modified by adding graphic layouts, annotations, and filters.
It features a drag-and-drop interface for creating data models from various data sources.
Importance of Data Visualization
Data visualization as a service assists any business by providing data most effectively. It involves taking raw data, modeling it, and displaying it to provide insights. Lets understand data visualization importance in detail:
1. Improving the Data Analysis
Report analysis supports business stakeholders in concentrating on the areas that require attention. Analysts can better comprehend the critical factors for their company by using graphical tools. A visual representation of data, whether in a sales report or marketing strategy, assists firms in increasing their profitability through more significant analysis and commercial decision-making.
2. Data Visualization Discovers Data Trends
The most essential thing that data visualization does is identify data trends. After all, it is much simpler to spot data patterns when all the data is set out in front of you in a visual format instead of data in a table. For example, the Tableau snapshot below shows the total sales made by each client in decreasing order. However, the color red implies loss, whereas the color gray denotes profit. As a result, it is extremely clear from this visualization that even if certain customers make large sales, they are still losing money. This would be tough to see from a table.3. Faster Decision Making
Visuals are more easily processed by humans than tedious tabular forms or reports. If the data communicates well, decision-makers can act on fresh data insights immediately. This speeds up decision-making and corporate growth at the same time.4. Making Sense of Difficult Data
Data visualization provides business users with insight into massive volumes of data. It helps them identify new patterns and faults in the data. Making sense of these patterns allows users to focus on regions that signal red flags or progress. This process, in turn, propels the company forward.Data Visualization Strategy
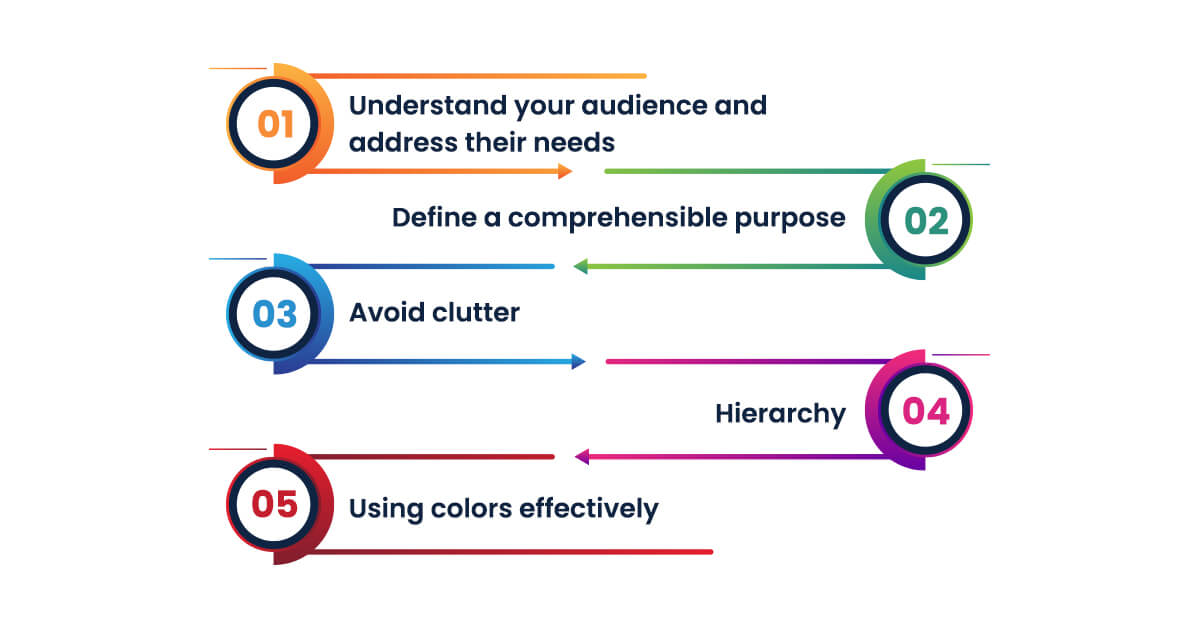
The key to success is to define the goal accurately. It entails using suitable procedures, formats, and design ideas.
Here are some data visualization strategies and best practices to help you get it all right:
Understand your audience and address their needs
A data visualization must be designed to communicate with a specific target audience. It should be appropriate for the target audience’s knowledge and needs. Businesses must comprehend their target market. They should assess how familiar the audience is with the concepts in the data and how readily the charts and graphs can be understood.
The needs of the target audience and what they intend to do with the information supplied should be understood, and only facts relevant to their needs should be highlighted.
It should be compatible with the audience’s knowledge and allow viewers to access and swiftly digest information. Consider if the audience is familiar with the core ideas offered by the statistics. Also, consider whether they have a background in STEM disciplines. Charts and graphs are more likely to be viewed daily in STEM fields.
Define a comprehensible purpose
Data visualization can assist in answering crucial strategic issues and give essential information that can aid in developing real-world solutions. It can be used to track performance, monitor behavior, and assess the efficiency of various activities. Taking the effort to clarify the purpose, priorities, and goals of the data visualization early on will make the end product more valuable and relevant to the specific target audience, saving you from producing needless visualizations. Determine what decisions you want the target audience to make and how frequently the data must be supplied. Data visualization should deliver actual value and assist in solving real issues by answering critical strategic questions.
It can be used to track performance, monitor consumer behavior, and assess the efficacy of operations, among other things. Identifying the aim and priorities at the start of a data visualization project will make the end product more valuable and save time producing needless images. Choose the best visual arrangement for your needs and embrace simplicity. Various charts, graphs, tables, and schemes are available to display data. It can be done by determining which type is ideal for visualizing the data. The proper approach will make the data displayed understandable and show it in the most accurate and relevant manner. It is essential to use the proper style of visualization that represents particular data. Since it is critical to transmit the correct facts to consumers most effectively.
Avoid clutter
The viewer should be able to receive the most critical information they want from the analytics dashboard with a short glance. They should be able to dig down to see more information when needed. Clear and simple analytics dashboards will bring more value than overly complicated ones.You should ensure that the user is not required to perform any needless computations or research to acquire insights from the dashboard. The dashboard should be manageable with widgets. Placing 6-8 widgets in a clear structure can assist in establishing adequate uniformity and comprehensiveness with minimal effort. Use 3 or 4 widgets initially to allow the user to realize and adopt the most critical information simply by looking at them. From there, you can use the additional widgets to see data supporting the primary widgets’ story. Using a minimalist design assists the user in focusing on the data displayed.
Hierarchy
Hierarchy is essential, especially in data visualization and dashboard design. As previously indicated, there is a predetermined widget arrangement that consumers will understand without more explanation. Graphical data and dashboards can be scanned with a suitable organization.Using colors effectively
Good style assists the user in better understanding the story and meaning behind the data by emphasizing critical areas of attention. Color is often utilized to express and differentiate information, and it has also been discovered to be an essential influence in human decision-making. When researchers examined how individuals reacted to various color combinations used in charts, they determined that palettes with minor color changes were more visually attractive. However, these palettes made the charts more difficult to study and obtain insights, eventually contradicting the objective of producing a visualization to present data.Remember that when we study colored data in graphs, charts, heat maps, tables, maps, and so on, lighter colors are associated with lower or median values. At the same time, darker colors are associated with higher or extreme values. Color can also be used for simple color coding, such as showing on-target performance in green and off-target performance in red. Combining or changing this can make grasping the data presented extremely difficult and paradoxical. A color palette matching your organization’s brand standards creates a consistent graphic language and experience for your users, contributing to the brand’s identity.
Process of Data Visualization
It is essential to follow a predefined data visualization process and data visualization fundamentals. It helps to connect with experts for proper data representation to ensure easy understanding and quick representation.
Step 1: Know Your Audience
Evaluate your audience’s expectations, background knowledge, and sources of information. This will assist you in determining how intricate and complex your images should be.
Step 2: Collect Data
Gather information from various sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and other documents. Ensure the information is accurate, complete, and valuable for your visual representation that appeals to the viewers.
Step 3: Clean Up Your Data
Correct any errors or missing pieces of your data. Identify and collect data from various sources. This stage is essential to the dependability and quality of your visualizations.
Step 4: Define Your Objective
Be specific about what you want to accomplish with your visualization. Having a defined aim assists in guiding the entire process, whether detecting patterns, comparing data, or conveying a story.
Step 5: Understand Your Data
Look closely at your data to see the patterns and relationships. This helps you decide what’s important to show in your visualization.
Step 6: Pick a Visual Style
Choose a way to show your data that makes sense. Think about the kind of data you have and the message you want to share. Based on that, Visuals and graphs can be created.
Step 7: Adjust Your Data
Change your data to fit the style you picked. This might mean combining data, adding new details, or converting data types.
Step 8: Create Your Visualization
Use tools like Tableau, matplotlib, or D3.js to build your visuals. Evaluating design patterns, colors, and labels is crucial to make them clear and easily understood.
Step 9: Get Feedback
Share your visualization with others and see what they think. Listen to their feedback and fix any problems or suggestions given by them to make the visualization more effective.
Step 10: Handle Big Data
If you’re dealing with a lot of data, find good ways to handle it efficiently. This could mean using unique technology or techniques to analyze and show the data.
Step 11: Make it Interactive
Let people interact with your visualization. Add things like filters or tools so they can explore the data independently. This makes it more exciting and helps them understand better.
Step 12: Keep It Simple
Make things simple enough, but also keep accuracy. If needed, add extra info so people understand the complexity of the data.
Step 13: Guide Your Audience
Use labels and legends to guide people through your visualization. Help them understand what they’re looking at and what’s important.
Step 14: Refine Your Work
Make improvements based on feedback or if the data changes. Think about how it looks and how people use it.
Step 15: Tell Your Story
Present your final visualization with a story that highlights the essential results. Ensure that it matches your initial goal and tells the story you wanted to share.
Major Industries Benefitted from Data Visualization
The data visualization can be utilized by diverse industries to ensure a smooth decision-making process. Let’s explore major industries that have benefited from data visualization technologies.
Health Care & Pharmaceuticals
Big data and cutting-edge cloud technologies are being invested in by pharma and the healthcare industry to use analytics to enhance patient care and happiness. The healthcare business has seen improvements in several areas. Healthcare data visualization examples include wearable trackers and remote patient monitoring (RPM), which assist in determining if patients are sticking to their treatment plans. It also helps in keeping track of treatments and prescribed medications.
Data gathered and processed over time provides complete data to doctors on their patient’s well-being and actionable insights. It facilitates shorter wait times and better service for medical professionals.
Strategies of Data Visualization to implement in Healthcare for better business operations:
1. Focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
2. Enhance Patient Engagement and Education
3. Optimize Resource Allocation and Budgeting
4. Streamline Clinical Decision-Making
5. Promote Data-Driven Culture and Collaboration
Government & Banks
The government uses particular computer analysis called analytics to improve lots of things for better understanding. They use big data sets to improve public services, like watching money markets, protecting the environment, and even finding bad guys who try to cheat. Banks also use these unique tools to make intelligent decisions when they trade money, check for risks, and stop bad things from happening with money.
Strategies of Data Visualization to implement in the Governmnet and Banking sector for better business operations:
Government:
1. Enhance Transparency and Public Engagement
2. Optimize Resource Allocation and Service Delivery
3. Streamline Internal Operations and Collaboration
Banking:
1. Customer Segmentation and Personalized Marketing
2. Operational Efficiency and Risk Management
3. Enhanced Customer Insights and Experience
Retail & Wholesale
In stores, they use these special computer tools to understand what customers want and ensure they have it ready. This helps stores beat their competition, keep customers happy, and sell more stuff by being smart about prices and making shopping better for everyone.
Strategies of Data Visualization to implement in the Retail and wholesale sector for better business operations:
1. Know Your KPIs and Target Audience:
2. Embrace Dashboards for Real-time Insights
3. Drill Down with Interactive Visualizations
4. Go Beyond Numbers: Tell Stories with Data
5. Empower Action with Accessible Tools
6. Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Cyber Security Data Visualization
In cyber security data visualization, experts use pictures to understand tricky computer stuff. Instead of boring lists and tables, they use incredible visuals like graphs or maps to see if something strange is happening with computers. This helps them work together, make quick decisions, and stop problems before they become significant issues.
Strategies of Data Visualization to implement in the Cyber Security sector for better business operations:
1. Real-time Threat Landscape Intelligence
2. Deep Dives into Incident Analysis
3. Simplifying Compliance Reporting
4. Engaging Stakeholders and Fostering Awareness
5. Optimizing Resource Allocation and Response
Conclusion
Mastering data visualization provides a bunch of opportunities in various industries. Data visualization is an advanced tool for analyzing and presenting data in an easy-to-understand form. It is an integral part of the business intelligence process. It helps various industries to make effective decisions. It visualizes vast volumes of complicated data using charts and graphs.
By using advanced tools and techniques, data visualization became the norm for presenting information to users via the business intelligence interface. This helps to navigate the vast data landscape, turning it into a compelling narrative. Through this, businesses can frame effective strategies to fuel continuous growth in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
FAQ
Data visualization is the method of expressing data using standard representations like graphs, plots, informational graphics, and animations. These visual representations of information illustrate complex data links and insights from data in an accessible manner.
There are several data visualization tools available that can be used to represent the data for different purposes
The following are the 10 best Data Visualization Tools
- Tableau
- Looker
- Zoho Analytics
- Sisense
- IBM Cognos Analytics
- Qlik Sense
- Domo
- Microsoft Power BI
- Klipfolio
- SAP Analytics Cloud
- Thoughtspot
Data visualization is important because it makes data easier to view, interact with, and comprehend. Regardless of complexity, a well-chosen representation may put all parties in agreement, even those with varying degrees of experience.
Data visualization is an effective way to showcase the data. It is advantageous to businesses but on the other hand, it also has a few disadvantages that need to be analyzed to ensure seamless workflow.
Advantages:
• Data Clarity and Understanding
• Analyzing Insights and Patterns
• Effective Decision-Making
• Smooth Engagement
• Seamless Communication
• Efficient data representation
Disadvantages:
• Misinterpretation of data
• Overcomplication
• Subjectivity to the technique utilized
• Technical Skill Requirement
• Data Limitations
• Tool Dependence
About Author

Bhavesh Parekh
Mr. Bhavesh Parekh is the Director of X-Byte Data Analytics, a rapidly growing Data Analytics Consulting and Data Visualization Service Company with the goal of transforming clients into successful enterprises. He believes that the client's success helps in the company's success. As a result, he constantly guarantees that X-Byte helps their clients' businesses realize their full potential by leveraging the expertise of his finest team and the standard development process he established for the firm.
Connect With Our Data Experts
Phone: +1 832-251-7311
Email: info@xbyteanalytics.com
Address: 10685-B Hazelhurst Dr., Houston, TX, 77043, USA


