Key Highlights:
- In most Databricks vs Snowflake comparisons, Databricks is more cost-efficient for engineering and AI workloads, while Snowflake is more predictable and cost-effective for BI and high-concurrency analytics.
- Databricks and Snowflake solve different problems. Databricks is built for data engineering, machine learning, and AI-driven workloads, while Snowflake is built for SQL analytics, reporting, and governed business intelligence at scale.
- The real difference between Databricks and Snowflake becomes clear when you map platforms to business functions.
The Databricks vs Snowflake conversation has matured, and in 2026, it’s no longer just a tooling debate. It’s a data architecture and business strategy decision.
Both Databricks and Snowflake sit at the center of modern enterprise data stacks. Both power mission-critical analytics. Both support AI workloads. And both are trusted by large, data-driven organizations.
Do you know, Snowflake and Databricks together hold a significant share in specialized cloud analytics segments, each capturing 15–20 % of market share in certain global cloud data platform analyses. This highlights their strong adoption compared to legacy systems and other cloud competitors.
Yet, many enterprises still struggle when it comes to choosing between them.
Why?
Because most comparisons focus on features instead of fit.
In reality, Databricks and Snowflake are built on fundamentally different philosophies:
- Databricks is optimized for engineering-heavy, AI-driven, Lakehouse-first organizations
- Snowflake is optimized for analytics-first, SQL-centric, business intelligence at scale
Treating them as interchangeable big data analytics platforms leads to:
- Over-engineered BI stacks
- Underpowered ML platforms
- Unexpected cost overruns
- Friction between data engineers, analysts, and business teams
If you are in this dilemma and are evaluating enterprise data analytics platforms, planning a cloud data platform comparison, or reassessing a data warehouse vs data lakehouse strategy, this blog is all you need.
What Is Databricks in 2026?
In 2026, Databricks is widely recognized as the leading data lakehouse and AI-ready analytics platform, powering some of the world’s most advanced data engineering, analytics, and machine learning initiatives.
Originally founded by the creators of Apache Spark in 2013, Databricks invented and popularized the Lakehouse architecture, a unified approach that combines the reliability and performance of data warehouses with the scalability and flexibility of data lakes.
It now serves thousands of large enterprise customers, many with over $1 million in annual spend, while integrating data engineering, data science, analytics, and AI workflows into a single operational and governed environment to break down data silos and accelerate value from data at scale.
How DataBricks Stands Out?
Databricks stands out as a unified data and AI platform built for organizations that go beyond traditional analytics. Rather than separating engineering, analytics, and machine learning into different systems, it brings them together under a lakehouse architecture. This enables teams to build data pipelines, run analytics, and deploy AI models on the same foundation. Below are the key capabilities that differentiate Databricks in modern enterprise environments.
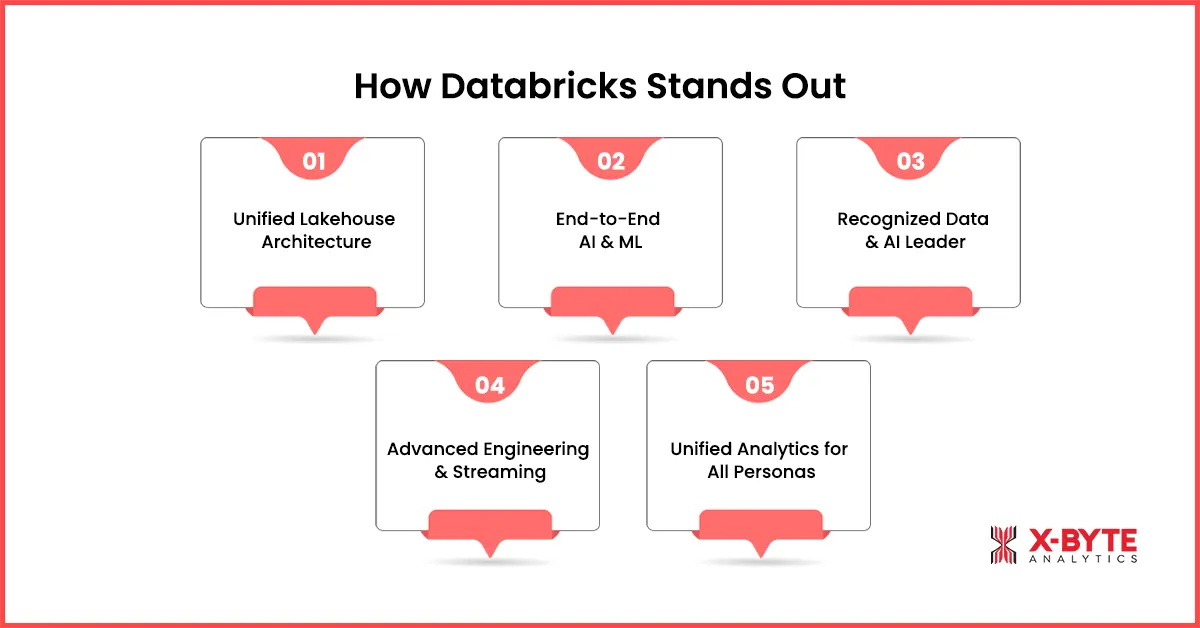
1. Unified Lakehouse Architecture
Databricks enables organizations to store raw, structured, and unstructured data in open formats such as Delta Lake and Parquet, while supporting ACID transactions and high-performance analytics traditionally associated with data warehouses.
This removes the need for complex ETL bottlenecks and redundant data copies, simplifying data pipelines and ensuring consistency across applications.
2. End-to-End AI and ML Support
With capabilities such as Databricks SQL, MLflow, Unity Catalog, and native generative AI tooling, the platform enables organizations to build, train, deploy, and monitor models on the same unified data foundation.
This is a step beyond traditional analytics: AI is no longer an add-on; it is first-class infrastructure.
Recent industry analyses indicate that enterprises are deploying significantly more AI models into production than in previous years, reflecting a shift from experimentation to operational AI at scale.
3. Recognized Leadership in Data and AI Platforms
Independent analyst firms continue to validate Databricks’ strategic positioning: In 2025, it was recognized as a Leader in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Data Science and Machine Learning Platforms, a testament to its comprehensive vision and execution in one of the most competitive segments of enterprise software.
4. Built for Advanced Data Engineering and Streaming Workloads
Databricks is designed to support large-scale data engineering workloads that extend beyond traditional batch analytics. This includes high-volume ingestion, complex transformations, and real-time or near-real-time streaming use cases.
By treating data engineering as a first-class workload, the platform enables teams to process both batch and streaming data using the same underlying engine and storage layer. This reduces architectural fragmentation and eliminates the need for separate streaming or preprocessing systems.
5. Unified Analytics Experience for Multiple Data Personas
Databricks supports a single, governed analytics environment where data engineers, analysts, and data scientists can work on the same datasets without duplication.
Engineers build pipelines and transformations, analysts query data using SQL through Databricks SQL, and data scientists develop models, all on the same lakehouse foundation. Rather than optimizing exclusively for analysts or engineers, Databricks is optimized for cross-functional data teams operating at scale.
What Is Snowflake in 2026?
In 2026, Snowflake is widely recognized as the leading cloud-native data warehouse and analytics-first data cloud, trusted by enterprises for high-performance SQL analytics, data sharing, and governed business intelligence at scale.
Founded in 2012 with a cloud-first mindset, Snowflake redefined enterprise analytics by introducing a fully managed architecture with separation of storage and compute, eliminating many of the operational challenges associated with traditional on-premise data warehouses.
Today, Snowflake serves thousands of global enterprises across industries, acting as the central analytics layer for organizations where business intelligence, reporting, and data collaboration are core priorities.
How Does Snowflake Stand Out?
Snowflake stands out as a cloud-native analytics platform purpose-built for modern enterprise data workloads. Unlike traditional data warehouses, it is designed for scalability, simplicity, and secure collaboration across teams. Its architecture and governance model make it especially effective for organizations that prioritize SQL analytics, reporting, and centralized data management.
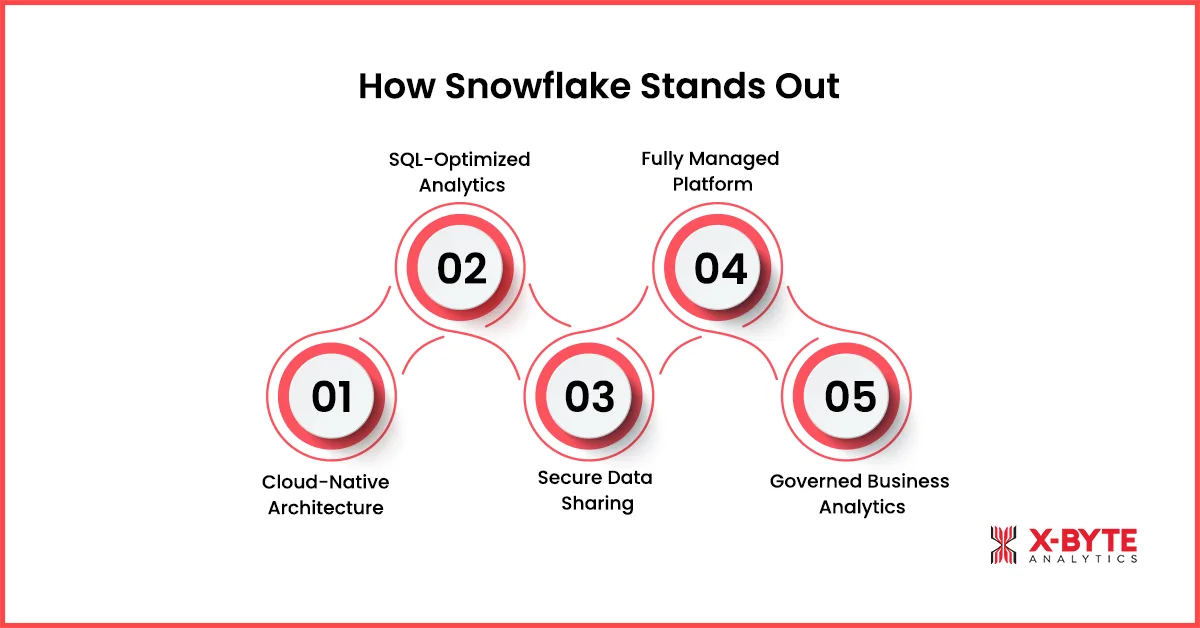
Below are the key capabilities that differentiate Snowflake from traditional data platforms and make it a preferred choice for analytics-driven enterprises:
1. Cloud-Native Data Warehouse Architecture
Snowflake is built as a true cloud-native data warehouse, with complete separation of storage and compute. Data is stored centrally, while compute runs on isolated virtual warehouses that can be scaled independently.
This architecture ensures predictable performance, strong workload isolation, and simplified capacity planning, even as analytics usage grows across multiple teams.
2. Analytics-First Platform Optimized for SQL Workloads
Snowflake is intentionally designed for SQL-based analytics and BI workloads. Analysts can run complex queries without worrying about infrastructure tuning, indexing strategies, or resource contention.
This makes Snowflake especially effective for organizations where dashboards, reporting, and ad hoc analysis are mission-critical and widely used across business teams.
3. Native Data Sharing and Secure Collaboration
One of Snowflake’s defining strengths is its ability to share live data securely without copying or moving it. Teams, partners, and customers can access governed datasets directly within Snowflake.
This capability enables cross-department analytics, partner data exchanges, and data marketplace use cases, while maintaining strict control over access and compliance.
4. Fully Managed Platform with Low Operational Overhead
Snowflake abstracts away nearly all infrastructure management. Scaling, performance optimization, availability, and maintenance are handled by the platform itself.
As a result, organizations can achieve fast time-to-value without building large platform engineering teams, making Snowflake attractive to enterprises that prioritize simplicity and operational efficiency.
5. Centralized, Governed Analytics for Business Teams
Snowflake provides a single, governed analytics environment where analysts and business users work with consistent, trusted data.
By centralizing analytics in one platform, Snowflake helps reduce metric discrepancies, improve data governance, and support analytics adoption beyond technical teams into the broader organization.
Databricks and Snowflake Use-Cases Comparison
Choosing between Databricks and Snowflake depends on how an organization uses data to drive decisions. While both platforms support modern cloud analytics, their strengths differ across machine learning, data engineering, reporting, and governance. Understanding real-world use cases helps clarify where each platform delivers the most value. Below is a practical comparison of how enterprises apply Databricks and Snowflake in different business scenarios.
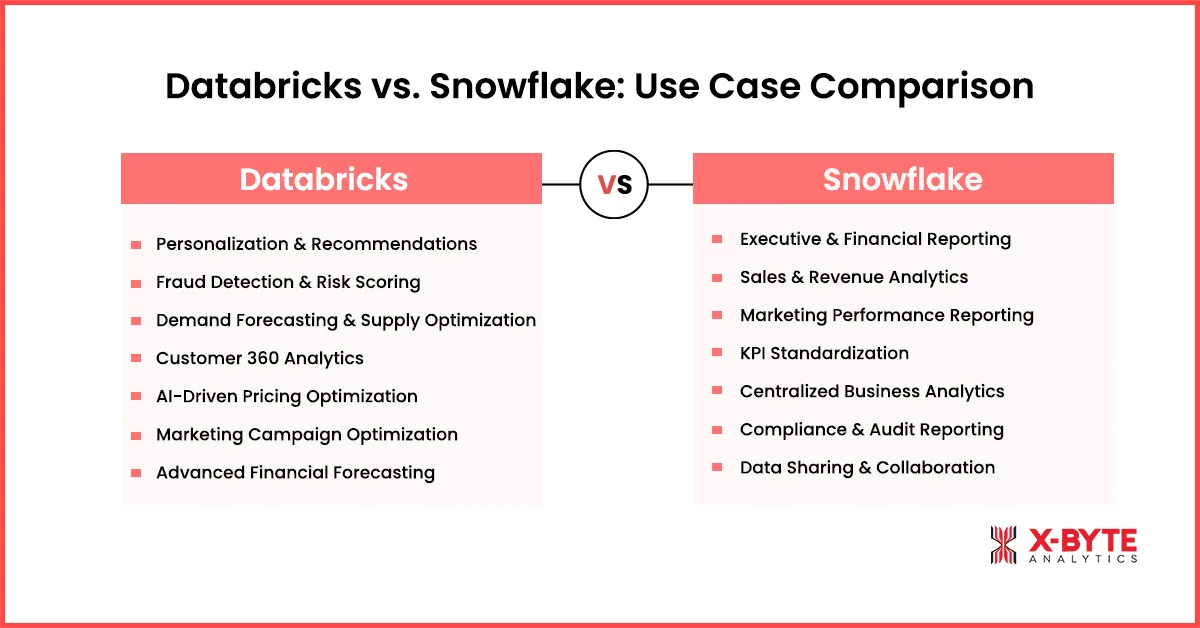
A. Databricks Use Cases
In the Databricks vs Snowflake debate, teams choose Databricks when analytics need to do more than power dashboards. Databricks use cases focus on data engineering, machine learning, real-time analytics, and AI-driven decisions, where teams work with large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
Let’s dig in to know more!
1. Product Personalization & Recommendation Systems
Business Problem: Customer experiences feel generic. Conversion rates plateau. Marketing and product teams lack real-time insight into user behavior.
How Databricks Is Used:
- Combine clickstream data, transaction history, and behavioral signals
- Train and deploy recommendation models continuously
- Update personalization logic as new data arrives
Business Impact:
- Higher conversion and engagement
- Faster experimentation with new product features
- Personalization driven by live data, not weekly reports
This is a classic case where Databricks and Snowflake diverge: Databricks supports the full ML lifecycle behind the product, not just analytics on top of it.
2. Fraud Detection and Risk Scoring
Business Problem: Fraud is detected too late, after losses occur. Rule-based systems don’t scale or adapt.
How Databricks Is Used:
- Ingest transaction and behavioral data in near real time
- Train models to detect anomalies and suspicious patterns
- Continuously retrain models as fraud tactics evolve
Business Impact:
- Reduced financial losses
- Faster fraud detection and response
- Lower dependence on manual reviews
This is a strong Databricks use case in regulated industries like fintech, insurance, and e-commerce.
3. Demand Forecasting & Supply Chain Optimization
Business Problem: Overstocking ties up capital. Understocking causes lost revenue. Forecasts rely on static historical data.
How Databricks Is Used:
- Combine historical sales, seasonality, promotions, and external signals
- Build predictive models that update frequently
- Run scenario analysis for pricing and inventory decisions
Business Impact:
- Better inventory planning
- Lower carrying costs
- Improved on-time fulfillment
This use case highlights why Databricks is often chosen in data lakehouse vs data warehouse decisions involving operational analytics.
4. Customer 360 and Behavioral Analytics
Business Problem: Customer data is fragmented across marketing, product, support, and sales systems.
How Databricks Is Used:
- Unify structured and semi-structured customer data
- Create a single, continuously updated customer view
- Enable analytics and modeling on the same dataset
Business Impact:
- Better segmentation and targeting
- More accurate churn prediction
- Consistent customer metrics across teams
This is a common enterprise data analytics scenario where Databricks enables both analytics and modeling without duplicating data.
5. AI-Powered Pricing and Revenue Optimization
Business Problem: Pricing decisions are slow, manual, or based on limited data.
How Databricks Is Used:
- Analyze historical pricing, demand elasticity, and competitor signals
- Train models to recommend optimal pricing
- Test and iterate pricing strategies quickly
Business Impact:
- Increased revenue per customer
- Faster response to market changes
- Data-driven pricing at scale
6. Marketing Attribution and Campaign Optimization
Business Problem: Marketing teams spend across multiple channels but struggle to see what actually drives revenue.
How Databricks Is Used:
- They combine ad platforms, website behavior, CRM data, and conversions in one place.
- Analyze full customer journeys and test attribution models instead of relying on last-click reporting.
Business Impact:
- Teams improve ROI
- Cut wasted spend
- Make faster campaign decisions
7. Advanced Financial Analytics and Forecasting
Business Problem: Finance teams rely on static forecasts and delayed reporting.
How Databricks Is Used:
- They run scenario analysis, revenue forecasting, and cost modeling on detailed, up-to-date data.
Business Impact:
- More accurate forecasts
- Faster planning cycles
- Better executive decision-making
B. Snow-Flake Use-Cases
In the Databricks vs Snowflake comparison, enterprises choose Snowflake when analytics, reporting, and data governance drive day-to-day decision-making. Snowflake use cases focus on SQL-based analytics, centralized reporting, and secure data sharing, making it a strong fit for organizations building an analytics-first cloud data platform for enterprise data analytics.
1. Executive and Financial Reporting
Business Problem: Executives and finance teams need fast, accurate, and consistent reporting for leadership reviews, board meetings, and financial close.
How Snowflake Is Used: They centralize financial, sales, and operational data and run high-concurrency SQL analytics without performance issues.
Business Impact:
- Faster close and reporting cycles
- Higher trust in executive metrics
- Better strategic decision-making
2. Sales Performance and Revenue Analytics
Business Problem: Sales leaders lack real-time visibility into pipeline health, quota attainment, and revenue trends.
How Snowflake Is Used: They analyze CRM, revenue, and forecasting data in one governed analytics layer and power dashboards used across sales and GTM teams.
Business Impact:
- More accurate revenue forecasts
- Better sales performance tracking
- Faster go-to-market decisions
3. Marketing Performance and Attribution Reporting
Business Problem: Marketing teams struggle to measure campaign effectiveness and channel ROI consistently.
How Snowflake Is Used: They consolidate campaign, web, and conversion data and run attribution and performance analysis through BI tools.
Business Impact:
- Clear visibility into marketing ROI
- Faster campaign optimization
- Reduced reliance on engineering teams
4. Company-Wide KPI Standardization
Business Problem: Different teams report different numbers for the same KPIs, leading to confusion and mistrust.
How Snowflake Is Used: They define shared data models and governed metrics that all teams query consistently.
Business Impact:
- One version of the truth
- Fewer internal data disputes
- Higher confidence in analytics
5. Centralized Analytics for Finance, Sales, and Operations
Business Problem: Analytics lives in silos, making cross-functional insights hard to achieve.
How Snowflake Is Used: They use Snowflake as a centralized cloud data warehouse that supports analytics across finance, sales, and operations from a single platform.
Business Impact:
- Improved cross-team alignment
- Faster operational insights
- Better enterprise-wide decision-making
6. Regulatory, Audit, and Compliance Reporting
Business Problem: Regulatory reporting requires accuracy, consistency, and auditability.
How Snowflake Is Used: They centralize governed datasets and generate repeatable, auditable reports for compliance and risk teams.
Business Impact:
- Reduced compliance risk
- Faster audit cycles
- Lower reporting effort
7. Partner and Customer Data Sharing
Business Problem: Sharing data with partners or customers often requires copying data and managing security risks.
How Snowflake Is Used: They securely share live, governed datasets without duplicating or exporting data.
Business Impact:
- Faster partner collaboration
- Lower data management costs
- Stronger data security and control
Transform Your Enterprise Data Platform With Databricks Experts
Databricks vs Snowflake: Key Differences
The Databricks vs Snowflake decision ultimately comes down to how an organization uses data to drive its business.
Databricks focuses on data engineering, machine learning, real-time analytics, and AI-driven systems, making it a strong fit for product-led and engineering-heavy organizations.
Snowflake focuses on SQL-based analytics, reporting, governance, and data sharing, making it ideal for analytics-first enterprises.
Here’s a structured comparison to make the differences clearer:
| Dimension | Databricks | Snowflake |
| Primary Role | End-to-end data lakehouse platform for engineering, analytics, and AI | Cloud-native data warehouse for analytics and reporting |
| Core Philosophy | Engineering-first, AI-first | Analytics-first, SQL-first |
| Best For | ML-driven products, real-time analytics, and advanced data engineering | BI, dashboards, reporting, and enterprise analytics |
| Architecture | Data lakehouse (open data formats + analytics + ML) | Cloud data warehouse with separate storage and compute |
| Data Types | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data | Primarily structured and semi-structured data |
| Primary Users | Data engineers, data scientists, ML teams | Data analysts, BI teams, business users |
| SQL & BI Support | Supported, but not the core focus | Core strength and primary use case |
| Machine Learning & AI | Native, end-to-end ML and GenAI workflows | Supported, but typically secondary to analytics |
| Real-Time & Streaming | Strong support for streaming and near–real-time use cases | Limited, mainly batch-oriented analytics |
| Data Governance | Centralized governance across analytics and ML workloads | Strong governance for analytics and reporting |
| Data Sharing | Supported, but not the primary differentiator | Native, secure data sharing without duplication |
| Operational Complexity | Requires a stronger platform and engineering expertise | Fully managed with low operational overhead |
| Cost Model | Compute-based, optimized for large-scale processing | Consumption-based, optimized for analytics workloads |
| Typical Business Use Cases | Personalization, fraud detection, pricing, forecasting, GenAI | Executive reporting, sales analytics, compliance, KPI tracking |
| Position in Enterprise Stack | Data and AI foundation | Central analytics and reporting layer |
| Ideal Organization Type | Product-led, AI-driven, engineering-heavy | Analytics-first, BI-driven, business-focused |
Databricks vs Snowflake: Which Is Cheaper in 2026?
In 2026, the Databricks vs Snowflake cost debate has a simple truth: both Databricks and Snowflake follow usage-based pricing, but they charge for very different things, and that difference drives real-world costs.
Below is how costs typically show up in practice.
Databricks: What You Actually Pay in 2026?
Databricks pricing revolves around DBUs (Databricks Units) plus underlying cloud compute.
- DBU pricing typically ranges from ~$0.07 to $0.65+ per DBU, depending on workload type (jobs, SQL, ML, GenAI) and plan.
- Compute (VMs) is billed separately by your cloud provider.
- Storage uses cloud object storage (S3, ADLS, GCS), usually $20–$25 per TB/month depending on region.
What This Means in Real Terms
- Small to mid-size teams often spend $1,000–$5,000/month for data engineering workloads.
- ML-heavy or large-scale pipelines commonly land in the $10,000–$40,000/month range.
- Very large AI platforms can exceed that, but costs scale with active compute, not idle time.
Where Databricks Stays Cheaper
- Batch ETL and large transformations
- Machine learning training and inference
- Streaming and near–real-time processing
- Very large datasets where storage cost matters
When clusters automatically shut down correctly, Databricks avoids paying for idle capacity, this is where teams save the most.
Snowflake: What You Actually Pay in 2026?
Snowflake pricing centers on credits for compute and managed storage.
- Compute credits typically cost ~$2 to $4 per credit, depending on edition and region.
- A medium virtual warehouse can consume 2–8 credits per hour while running.
- Storage usually falls between $23–$40 per TB/month, compressed but fully managed.
What This Means in Real Terms
- Light analytics or small BI teams often spend $1,500–$5,000/month.
- Enterprise BI environments with many dashboards and users often run $15,000–$50,000/month.
- Costs rise quickly if warehouses stay running or auto-scale aggressively.
Where Snowflake Stays Cheaper
- High-concurrency BI and dashboards
- Predictable SQL analytics workloads
- Finance, sales, and exec reporting
- Organizations that want minimal platform management
Snowflake’s strength is predictability for analytics, not raw compute efficiency.
The Cost Trap Most Teams Fall Into
Most cost overruns in Databricks vs Snowflake comparisons come from misuse, not pricing.
- Using Snowflake for heavy ETL, ML, or streaming often leads to runaway credit consumption.
- Using Databricks as a BI-only platform drives up costs due to always-on clusters and concurrency pressure.
Both platforms punish teams when they get used outside their core strengths.
Drive Smarter Business Decisions With Snowflake Experts
Which One Should You Choose: Databricks or Snowflake?
Choosing between Databricks and Snowflake depends on how your organization uses data to create value. While both platforms support modern cloud analytics, they are optimized for different priorities, AI-driven innovation versus analytics-driven decision-making. The right choice depends on your workloads, team structure, and long-term data strategy. Below is a practical framework to help guide your decision.
A. Choose Databricks If Your Business Runs on Data and AI
You should choose Databricks if your organization treats data as a product and innovation engine, not just a reporting asset.
Databricks Is the Better Choice When:
- Data engineering pipelines are complex and large-scale
- Machine learning, AI, or GenAI drives business value
- You require real-time or near–real-time analytics
- Teams work with structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data
- You are building a data lakehouse instead of a traditional warehouse
Typical Databricks-Driven Outcomes Include:
- Product personalization and recommendation systems
- Pricing, forecasting, and optimization models
- Fraud detection and risk scoring
- AI-powered decision systems
In a data warehouse vs data lakehouse evaluation, Databricks fits organizations that want one platform for engineering, analytics, and AI.
B. Choose Snowflake If Your Business Runs on Analytics and Decisions
You should choose Snowflake if your organization prioritizes analytics, reporting, governance, and data sharing across the business.
Snowflake Is the Better Choice When:
- SQL analytics and BI dominate daily workloads
- Finance, sales, and leadership teams rely on dashboards
- Many users query data at the same time
- Governance, compliance, and metric consistency matter most
- You want a fully managed cloud data warehouse with low operational overhead
Typical Snowflake-Driven Outcomes Include:
- Executive and financial reporting
- Sales and revenue analytics
- Marketing performance reporting
- Regulatory and compliance reporting
- Secure partner and customer data sharing
In a cloud data platform comparison, Snowflake fits analytics-first organizations that need reliable, scalable decision support.
Why Enterprises Choose Both Databricks and Snowflake in 2026?
In 2026, many large organizations use Databricks and Snowflake together, not as competitors but as complements.
A Common Pattern Looks Like This:
- Databricks handles data ingestion, transformation, ML, and AI workloads
- Snowflake serves as the central analytics and reporting layer for business teams
This Approach Allows Organizations To:
- Optimize costs by workload type
- Avoid forcing one platform to do everything
- Scale both innovation and analytics independently
Conclusion
The Databricks vs Snowflake decision becomes clearer when organizations move beyond feature comparisons and focus on how data is actually used across the business. Databricks is the stronger fit where data engineering, machine learning, and AI-driven workloads are central. Snowflake consulting service ideal where analytics, reporting, and governed access power day-to-day business decisions.
If you are still overwhelmed and are looking for professional assistance, then our team at X-Byte Analytics can help you out. We analyze real workloads and use-cases, cost patterns, long-term goal, etc to help you make the right decision.
Our role is to bring clarity to platform choices, design practical architectures, and help organizations build data foundations that are easier to operate and grow.
To learn more about how we can support your data strategy, connect with our data experts today.